In the world of electrical systems, safety is paramount. One crucial aspect of electrical safety is proper grounding. Grounding helps prevent electrical shock, fires, and equipment damage by providing a low-resistance path for electrical currents to flow into the earth. However, without appropriate understanding and adherence to grounding hazards and labeling requirements, potential dangers can arise. With May being Electrical Safety Month, it’s a fitting time to explore the significance of electrical grounding hazards and the labeling requirements that ensure safety in electrical systems.
Understanding Electrical Grounding Hazards
Electrical grounding hazards occur when the ground connection in an electrical system is compromised or inadequate. These hazards can result in risks like:
- Electric Shock: Without proper grounding, electrical currents may flow through unintended paths, such as equipment casings or human bodies, leading to severe electric shock injuries or even fatalities.
- Fire Hazards: Inadequate grounding increases the risk of electrical fires. Faulty wiring, improper equipment grounding, or lightning strikes can cause electrical surges, leading to overheating and potential fires.
- Equipment Damage: Grounding plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive electrical equipment from voltage fluctuations and static electricity. In the absence of proper grounding and stabilization, equipment may experience malfunctions, damage, or premature failure.

Labeling Requirements for Electrical Grounding
To mitigate grounding hazards and ensure safety, electrical systems must adhere to specific labeling requirements. These labels serve as visual indicators and provide critical information about the grounding configuration and safety measures. Clear and visible warning labels must be affixed to all electrical enclosures, control panels, and equipment. These labels should include standard safety symbols and appropriate text, (such as "Danger: High Voltage," "Grounding Required," or "Do Not Remove Grounding Connection" as well as complete word messages to explain the nature of the hazard and how to avoid it). Safety labels and warnings can help to draw attention to potential hazards and remind individuals to follow safety protocols.
Here are some essential labeling requirements for electrical grounding:
- Grounding Symbol: Labels should prominently display grounding symbols. There are various globally-standardized options available – continue reading for more details!
- Grounding Connection Point: Labels should clearly identify the specific location where the grounding conductor is connected, such as a grounding bus bar or a designated grounding terminal.
- Testing and Inspection Dates: Your grounding systems should also include labels that indicate the dates of testing and inspection, providing a record of when the grounding system was last checked for proper functioning. Regular inspections are crucial to identify potential hazards and ensure ongoing safety.
- Compliance Standards: Labels should include or be checked for reference or compliance to applicable standards and regulations governing electrical grounding, such as the National Electrical Code (NEC), ANSI, ISO, or local building codes. Compliance with these standards helps ensure that grounding requirements are met.
How to Select the Right Grounding Symbol
Globally standardized symbols are available for you in two categories, those that identify functions and controls, and those that identify safety concerns.
Symbols are standardized worldwide by two highly-active global committees. ISO/TC 145 is the horizontal committee of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that addresses standardization of non-electrical function and control symbols and all safety symbols. The International Electrotechnical Commission’s IEC SC3C committee defines function and control symbols for electrical equipment.
Here’s how these global symbol standards are related and differ:
- Non-electrical function and control symbols are standardized in ISO 7000. Electrical function and control symbols are standardized in IEC 60417. Both standards are titled, ‘Graphical symbols for use on equipment.’ Safety symbols are standardized in ISO 7010.
- ISO/IEC function and control symbols tend to be more abstract whereas the ISO safety symbols are typically more representational in form.
- ISO safety symbols use a colored surround shape (circle, square or triangle) to define their overall safety function and to make these symbols more easily noticed and recognized.
- ISO/IEC function and control symbols are designed according to a strictly defined grid template that standardizes the size, shape and line thickness of the symbol’s elements. This helps in obtaining both uniformity and maximum visual “legibility” for these symbols, many of which are used in small sizes on control buttons and small labels.
To illustrate these points, take a look, below, at the three IEC function/control symbols used to identify ground connections. All three symbols are related by their similar vertical/horizontal design element and they are similarly abstract. But the use of the curved design element in 5018 and 5019 easily differentiates one symbol from another.
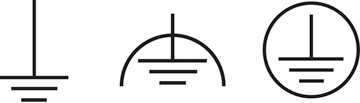
IEC 60417 ground symbols. From left to right: IEC No. 5017; IEC No. 5018; IEC No. 5019
Here are the precise definitions for each symbol:
- No. 5017 Earth (ground): Identifies an earth (ground) terminal in cases where neither the symbol 5018 nor 5019 is explicitly stated.
- No. 5018 Noiseless (clean) earth (ground): Identifies a noiseless (clean) earth (ground) terminal, e.g. a specially designed earthing (grounding) system to avoid causing malfunction of the equipment.
- No. 5019 Protective earth (ground): Identifies any terminal which is intended for connection to an external conductor for protection against electrical shock in case of a fault, or the terminal of a protective earth (ground) electrode.
These worldwide symbol standards let you conform at the outset without having to reinvent the process of properly identifying functions, controls, and safety concerns each time you design a product. Further, from the product user’s viewpoint there is greater certainty of meaning when seeing familiar, standardized symbols, which is why they have been growing in popularity over the years as workplaces and machine users continue to diversify.
Benefits of Proper Grounding Labeling
Adhering to proper grounding labeling requirements brings numerous benefits to electrical systems:
- Enhanced Safety: Clear and accurate grounding labels ensure that individuals working with or around electrical equipment can identify grounded components, minimizing the risk of electric shock and other hazards.
- Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Proper labeling enables efficient maintenance and troubleshooting by providing technicians with accurate information about grounding configurations. This facilitates quicker identification of faults and promotes timely repairs, minimizing downtime and ensuring the smooth operation of electrical systems.
- Compliance and Liability: Following grounding labeling requirements demonstrates compliance with industry standards and regulations. This helps mitigate potential legal and liability issues by ensuring that electrical systems meet safety guidelines.
Your Partner in Electrical Safety
Electrical grounding hazards can pose significant risks to individuals, property, and electrical equipment. By understanding these hazards and adhering to proper grounding labeling requirements, we can create a safer environment within electrical systems. Accurate labeling ensures that electrical components are grounded correctly, helping prevent electric shocks, fires, and equipment damage.
